Image source: YouTube
Table of Contents
- Introduction - AI, ML, DL, and GenAI
- AI Glossary
- AI Knowledge vs Skill
- AI Tools and Products
- TODO
- Some facts
- References
- AI Tools
Introduction - AI, ML, DL, and GenAI
As artificial intelligence continues to spread throughout every industry, it’s easy to get caught up in the lingo — AI, ML, DL, GenAI. what do they all mean, and how are they different? This piece demystifies the key terms and concepts so you can have a clear understanding of the world of AI. Whether you’re new to the industry or simply need a refresher on the basics, this glossary-driven primer will bring you up to date on the terminology of AI and machine learning.
AI Glossary
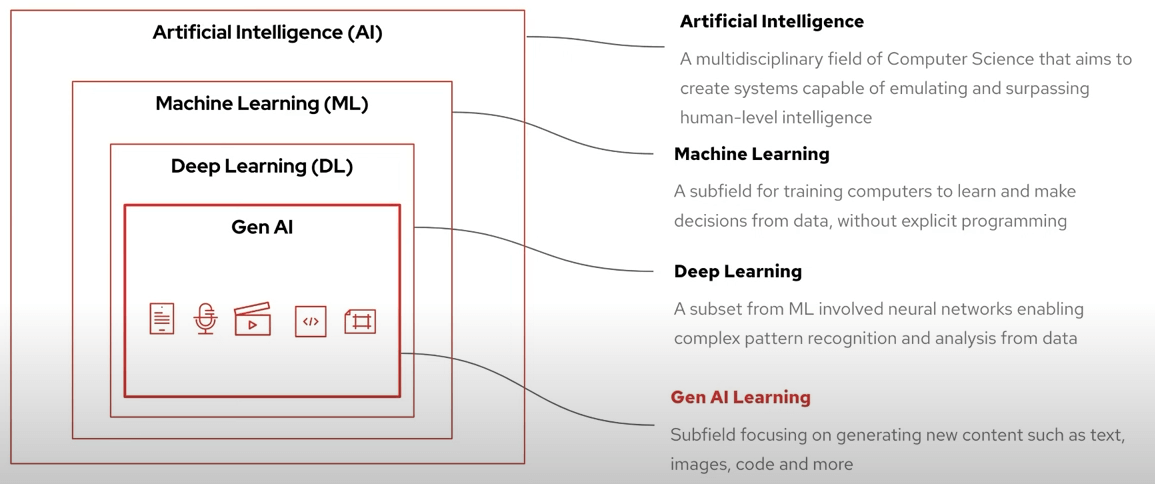
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The broader field of creating intelligent agents, aiming to mimic human intelligence.
Machine Learning (ML)
A subset of AI focused on teaching computers to learn from data without explicit programming.
Deep Learning (DL)
A subset of ML using artificial neural networks to analyze complex patterns in data.
Generative AI (Gen AI)
A subfield focused on creating new content, such as text, images, or code, based on learned patterns.
LAB (Large-scale Alignment for chatBots)
LAB is a research approach that focuses on making chatbot behavior harmonize with human values, goals, and expectations — at scale. While more powerful chatbots are possible, it’s no longer enough to just train them on large data sets. They need to be able to respond usefully, safely, and in line with user intent. LAB consists of model refinements through methodologies such as Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), instruction tuning, and preference modeling, to ensure responses are well-suited, accurate, and in line with what humans indeed desire.
At a large scale, this alignment becomes more complex — you’re not just adjusting responses for one use case, but ensuring consistent and ethical behavior across many domains, languages, and cultures. LAB plays a key role in building trustworthy AI assistants, especially those used in customer support, education, healthcare, and other high-impact areas.
LLM - Large Language Models
LLMs are extremely sophisticated AI models that have been trained on massive amounts of text data to understand and generate human-like language. These models, like GPT (by OpenAI) or BERT (by Google), learn to identify patterns, grammar, facts, reasoning, and context from books, websites, articles, etc. After being taught, they will be able to perform almost all language tasks such as answering questions, code programming, abstracting text, translating from other languages, and even chatting — all without any direct programming of them.
Large" in LLM refers to both the model size (millions or even billions of parameters) and the size of the data they are trained on. Because of this scale, LLMs can generalize well across domains and learn about a multitude of different user needs and therefore become a key part of modern AI applications like chatbots, virtual assistants, and content generation software.
Gen AI - Generative Artificial Intelligence
Generative AI or Gen AI is one of the subcategories of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating new knowledge — including text, pictures, sound, video, or even programming code — instead of just analyzing or sorting existing data. Powered by models such as GPT, DALL·E, and Stable Diffusion, Gen AI is trained from enormous datasets and creates new output based on learned patterns. For example, it can generate a story, design a logo, write a song, or generate photorealistic images given a simple text input.
What sets Gen AI apart is the ability to mimic creativity and provide output that appears to be human-made. It’s being used in every industry — marketing, design, software coding, education, and so on. While it holds out great promises, it raises basic questions regarding originality, bias, and usage, especially as the output gets more and more indistinguishable from humans’ work.
AI Inference
AI Inference is the process of using a machine learning model that has been trained on data to make predictions or decisions on new, unseen input. After large datasets have conditioned a model, inference is deploying the model, with the model applying the knowledge that it learned during training to real-world inputs. For example, an AI model trained to classify objects in images will perform inference when it looks at a new image and classifies the objects in it. Inference can be done in various settings, such as cloud servers, edge devices, or even smartphones, based on use case and performance requirements. It is an important step in AI implementation, where usefulness of the model is validated by how well and effectively it analyses data. and provides actionable insights.
AI Ethic
AI Ethics is the study and practice of ensuring artificial intelligence systems are used and created in ways that are fair, transparent, and responsible. AI Ethics deals with the process of making sure that AI doesn’t hurt people, discriminate in unfair ways, or make choices that cannot be understood. Since AI models are taught from large data sets — typically full of human prejudice or holes in the information — there’s a real danger that those imperfections are passed on to computers. AI ethics is an approach to managing how we create, test, and deploy AI, taking into account human values and social consideration.
Deepfakes
Deepfakes are media — predominantly images and videos — altered by AI to depict people, activities, or things in realistic but false ways. Advances in generative AI, such as neural networks and deep learning, have made it exponentially easier to create manipulated media that predominantly look very real and hard to distinguish from authentic content. As technology advances, the bar for producing deepfakes has been brought down, and almost anyone with little technical knowledge can now produce realistic but misleading content. This is especially worrying in environments such as trust, security, and disinformation since deepfakes have the potential to be utilized in shaping opinion, spreading lies, or damaging reputations. The widespread availability of deepfake production tools presents an ever-more serious threat to the authenticity of digital media and endangers individuals, institutions, and societies as a whole.
AI Knowledge vs Skill
Knowledge in AI:
- Knowledge represents the information and data that an AI system has access to, including facts, rules, and concepts about the world or a specific domain. It’s the foundational material that the AI uses to make decisions, predictions, and perform tasks.
- AI systems accumulate knowledge through data training (e.g., large datasets of text, images, or structured data) and can retrieve and apply this knowledge when required.
- Knowledge can be encoded as rules (in rule-based systems) or derived from patterns in data (in machine learning systems).
Examples:
- A language model like GPT is trained on vast amounts of text data, providing it with knowledge about grammar, facts, and even context.
- A medical diagnostic AI might have knowledge about symptoms, diseases, and treatments stored in its database or learned from medical literature.
Skill in AI:
- Skill refers to the ability of an AI to apply knowledge effectively to perform tasks or solve problems. It involves leveraging knowledge in a way that demonstrates proficiency in a specific task or set of tasks.
- AI develops skills through training, experience, and fine-tuning. Skill in AI can be thought of as the execution part, where the system demonstrates its capability to solve real-world problems using the knowledge it possesses.
Examples:
- A self-driving car’s ability to navigate roads by understanding traffic rules and reacting to real-time conditions.
- A machine learning model’s skill to recognize objects in images, using knowledge about how certain objects appear.
Relationship Between Knowledge and Skill in AI:
- Knowledge is the foundation, while skill is the application of that knowledge.
- An AI system may have vast knowledge but limited skill if it cannot effectively use the information to solve tasks.
- Conversely, a highly skilled AI must be backed by a strong knowledge base to perform its tasks accurately and consistently.
AI Tools and Products
InstructLab
InstructLab is a game-changer for enhancing large language models (LLMs). This open-source project, co-created by IBM and Red Hat, makes it easier to align LLMs with user intent, opening up possibilities for innovative AI applications.
Podman AI Lab
Podman AI Lab is Red Hat’s answer to simplifying the AI development process. This extension provides a local environment with essential open-source tools and curated recipes to guide you through building AI solutions.
Example Use Cases
- Running a Jupyter Notebook preloaded with TensorFlow or PyTorch
- Testing open-source LLMs locally in a container
- Prototyping AI-powered apps with minimal setup
- Learning or teaching AI/ML concepts using clean, reproducible environments
Podman AI Lab vs Docker
- Podman is rootless by default, so it’s more secure for personal or educational setups.
- No daemon needed — Podman doesn’t require a background service like Docker, making it lightweight and easier to manage.
- Fully open source, with better integration into Linux-native environments (especially for Fedora, RHEL, etc.)
- With Podman Desktop + AI Lab, the experience is user-friendly and great for quick local AI testing — without needing the cloud or expensive GPU clusters.
Red Hat OpenShift AI
Red Hat OpenShift AI is a powerful platform for deploying and scaling AI applications across hybrid cloud environments. Built on open-source technologies, it offers a trusted foundation for teams to experiment, serve models, and deliver innovative AI-driven apps.
TODO
– AI Model Types
Linear regression models - TODO
What is unlabeled data - TODO
AI Bias, Fairness, discrimination - TODO
AI hallucination - TODO
Human in the loop and human over the loop
AI Definition
Wat is adversarial-robustness-toolbox (ART) https://github.com/IBM/adversarial-robustness-toolbox
Some facts
- Llama2–70B model — a large language model released by Meta.ai.
References
- InstructLab Project
- InstructLab Taxonomy Repo
- InstructLab Repo
- JJ and Paul continue introducing and getting started with InstructLab (2024) (Video)
- InstructLab – “Ever imagined the ease of tuning pre-trained LLMs? InstructLab makes it a reality. Let’s delve into how it sets itself apart from other model tuning methods.” (Blog)
- Generative AI Development with Podman AI Lab, InstructLab, & OpenShift AI (Video)
- Glossary of artificial intelligence
AI Tools
- Cluely